- EARLY DEPLOYMENT
- DEVOPS
- TESTING
How to do earlier deployment and testing for a distribution platform
Oct 23, 2025
-
Emilia Skonieczna
-
9 minutes

What does software distribution really need? Speed, reliability, and flexibility.
But are those the only things that matter? Not quite - it's a complex process with many moving parts.
Early deployment and testing practices help teams identify problems before users are affected. The result? Higher release quality.
Looking at it from another angle, by deploying features ahead of the full release, teams can validate functionality in realistic environments and roll out updates with greater confidence.
So what should you know about it?
Early deployment is the process of rolling out new code or functionality before the official public launch. It allows teams to verify performance, stability, and compatibility under near-production conditions.
Usually, this happens in test or staging environments, where teams can simulate real usage without affecting end users.
This helps close the gap between development and production. So the potential problems can be caught early.
The key goal is simple: make it work before it goes live.
In a distribution platform, early deployment means separating release from deployment. In other words, new code can be deployed to servers and infrastructure ahead of time, but it's not active or visible to users yet.
By separating these two steps, it's easier to manage risk and prepare updates - even on a large scale - without disruptions.
Teams can roll out infrastructure changes in advance, monitor system behavior in a controlled way, and turn features on when everything is ready.
That's exactly why early deployment matters.

Unlike traditional release cycles - where deployment and release happen at the same time - early deployment relies on feature flag rollouts and shadow deployment.
Feature flags enable selective activation of new functionality for specific user groups, while shadow deployment runs new versions alongside live systems to observe performance without affecting users.
By combining these techniques, you can achieve faster, safer, and more adaptable early deployment compared to conventional methods.
Early testing is like a safety net. It strengthens distribution platforms through different testing methods like functional and regression testing, and by running automated test suites on staging servers. This helps expose integration and performance problems ahead of full release.
It ensures that issues are caught before users are affected.
If you use early testing, you can reduce several key risks like:
unanticipated bugs
deployment failures under load
last-minute firefighting
It also reduces release-day pressure by surfacing defects early, helps create faster feedback loops from QA and stakeholders, and enables early detection of integration issues.
As a result, you'll get improved cross-platform reliability and more stable system behavior - even before going live.
Setting up a CI/CD pipeline for early testing starts with version control (Git) and a CI service like GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins.
Each code change triggers automated builds and testing stages - including unit testing, integration testing, and end-to-end testing - all defined in YAML configs.
These steps create build artifacts that are deployed to pre-production environments or staging servers for verification in a controlled environment before the software is released.
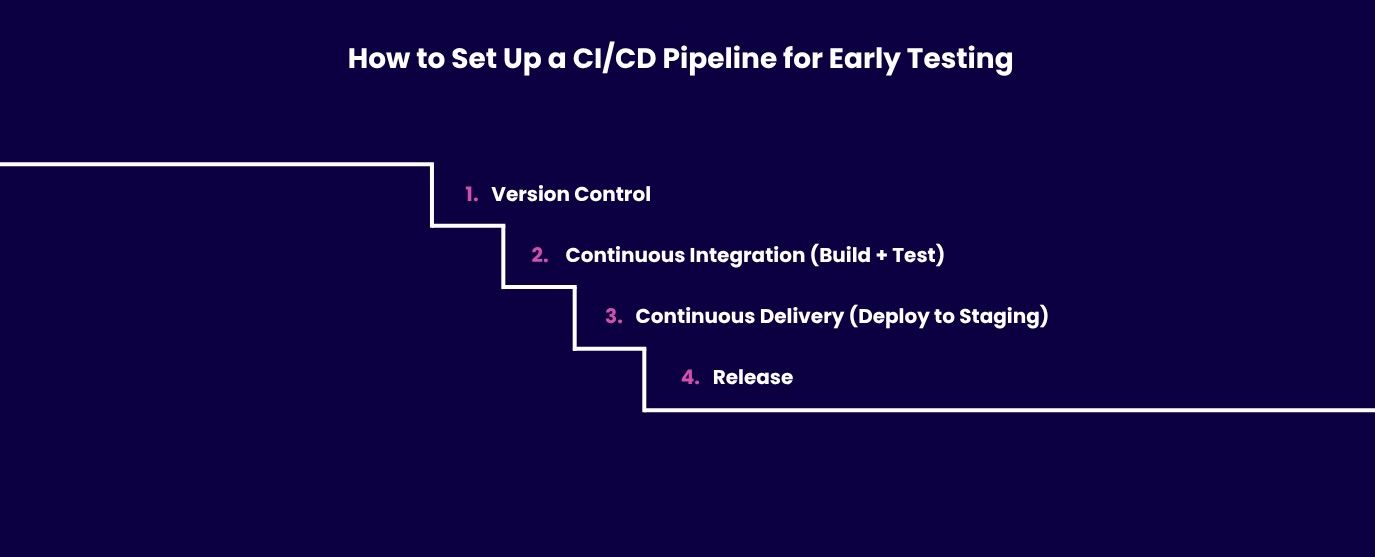
A reliable pipeline includes several key components:
automated testing stages
a deployment to staging step
conditional production releases
It supports continuous testing throughout the software development life cycle, which helps developers identify and fix bugs early.
Thanks to this, you can be sure that the software is verified and ready for deployment long before it reaches the production environment. It improves both quality and software delivery speed.
Automation minimizes manual effort and reduces human error. Quite helpful, right?
With the right deployment and monitoring tools, teams can test, get feedback, and fix issues faster. Automation also makes it easier to run canary testing - trying new software with a small group of users first to make sure everything stays stable.
Modern DevOps specialists rely on specialized tools that let them move fast without losing control - releasing faster with less risk.
LaunchDarkly uses feature flags to control how and when new features reach users, which allows teams to deploy code early while keeping new functionality hidden until it's ready.
Meanwhile, Split.io supports A/B testing and gradual rollouts, which allows safe validation before a full launch.
What do you gain?
Earlier deployment with a better user experience.
It can also simplify your deployment strategy and make early and safe releases part of everyday work.
Consistency is key. Argo CD provides GitOps deployments, keeping environments consistent and syncing changes from code to production.
If you pair it with Terraform and Ansible for infrastructure as code, you can adjust configurations and provision environments safely in advance.
I'd call that a win-win - predictable deployment with no surprises.

Safe experimentation starts with a controlled environment.
Docker and Kubernetes, through containerization and orchestration, make it possible to create isolated setups that mirror real systems. This allows teams to test and improve each software product before a full rollout.
They also support performance testing - giving developers the confidence to innovate without breaking what's already working.
Instead of exposing a risky feature to everyone at once, you can wrap it in a toggle and decide who sees it - and when. That's why you need feature flags. They let you deploy code early and still keep everything under control.
This way, you can test functionality in production-like conditions without endangering stability.
Quick tips:
Wrap risky features in toggles so you can disable or adjust them instantly.
Gradually enable features by user segment to collect feedback before full release.
Feature flags separate deployment from release. This means that the code is already live, but not visible to all users - only to a selected group. That's how you can validate performance and behavior step by step.
If something doesn't go according to plan, you can use kill switches for a fast rollback. This way, you can react immediately without rolling out a new build or affecting users.
Developers usually use three kinds of toggles:
Release toggles for gradually rolling out new functionality
Ops toggles for managing configuration or performance settings
Experiment toggles for A/B or canary testing
Log feature usage for monitoring to see how users interact with new functionality and to verify that everything behaves as expected.
A stable staging environment bridges the gap between development and production. It provides a safe space to verify new code, integrations, and configurations before anything goes live.
Once again, consistency is crucial here - the closer staging mirrors production, the more reliable your results will be.

Through staging, teams can validate the full system under conditions that closely resemble production. It's the place where you run comprehensive testing to verify stability, security, and reliability before a release.
After each successful build automatic deployment keeps the process fast, consistent, and error-free - ensuring every version is truly ready for production.
An effective staging environment should mirror your production infrastructure - including network, setup, configuration, and dependencies.
This way, developers can catch issues that wouldn't appear in simpler test setups. This helps ensure that your software behaves predictably once it's deployed to users.
Every successful deployment usually follows a clear, repeatable process. So what does it actually look like?
1. Version and build the code
Start with version control tools like Git to track every change. Each commit triggers an automated build that compiles the latest code into ready-to-test artifacts.
2. Test early and often
Run automated tests - unit, integration, and end-to-end - to validate functionality and catch issues early. Continuous testing ensures quality at every stage.
3. Deploy to staging
Push the build to a staging environment that mirrors production. This helps verify configuration, integrations, and performance under realistic conditions before going live.
4. Validate and monitor
Use feature flags, canary testing, and performance benchmarks to validate behavior and monitor stability. This is where you confirm that the system behaves as expected before a full release.
5. Release and automate
After each successful build, automated deployment keeps the process fast, consistent, and error-free - and makes rollback simple if something goes wrong.

Why exactly do startups need DevOps, and when is the right time to implement it? The answers you've been searching for start here.

Deploy smart, not stressed. Are Friday releases a real risk or just a myth? Let’s find out.

Discover how telemetry, monitoring, and analysis work together to transmit data from remote sources, optimizing system performance and enhancing application health.